Health monitoring of an infrastructure is a key element of day to day operations, knowing if something is healthy or unhealthy can make the difference between business impact or remediation steps to prevent any impact ot the business.
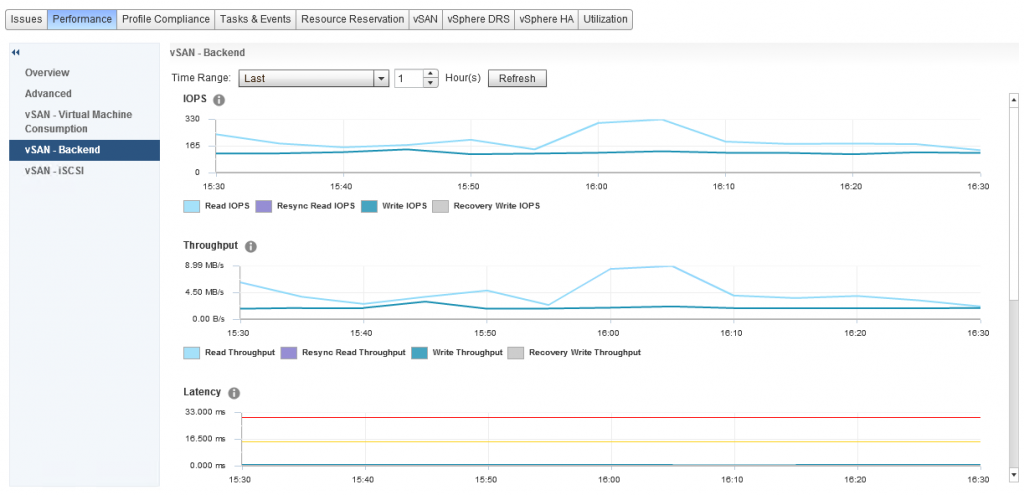
There are three ways you can monitor the health of vSAN, the native Health Service which is built into the vSphere UI, vRealize Operations (vROPS), and the API all of which have advantages and disadvantages over the other, for the first part we are going to cover the Health UI which is incorporated into the vSphere UI.
vSAN Health Service
In the current release of vSAN (6.6.1) there are two aspects to the Health Service, an Offline version and an Online version, the Offline version is embedded into the vCenter UI Code and any new features are added to this when patches/releases/updates for vSphere are  released. The Online portion of the Health UI is more dynamic, newer health variables are added as part of the Customer Experience and Improvement Program (CEIP), there is a major advantage to using the Online version in the fact that critical patch releases for vSAN can be alerted through the Health UI which is a really cool feature, it also dynamically adds new alarms to vCenter as part of the health reporting, as VMware understands and gets feedback on how customers are using vSAN, VMware can create alarms dynamically to alert/avoid situations that are a cause for concern.
released. The Online portion of the Health UI is more dynamic, newer health variables are added as part of the Customer Experience and Improvement Program (CEIP), there is a major advantage to using the Online version in the fact that critical patch releases for vSAN can be alerted through the Health UI which is a really cool feature, it also dynamically adds new alarms to vCenter as part of the health reporting, as VMware understands and gets feedback on how customers are using vSAN, VMware can create alarms dynamically to alert/avoid situations that are a cause for concern.
In order to use the Online portion of the health service you need to opt in to the CEIP program, which is as simple as ensuring your vCenter server has internet capability and you have provided a myvmware account credentials. A lot of customers are concerned with having their vCenter server having the ability to connect out to the internet, as a workaround I recommend a method where vCenter only has an allowed rule to connect to vmware.com addresses such as a proxy server or white list.
The health service is designed to report on all aspects of vSAN health, and trigger alarms in vCenter to alert you to anything that you should pay attention to, in the previous screenshot, you will  notice that I have a warning against the cluster, this is due to the cluster disks not being evenly balanced due to me placing two hosts into maintenance mode to perform firmware updates, as you can see from the screenshot on the right, this has also triggered an alarm in vCenter.
notice that I have a warning against the cluster, this is due to the cluster disks not being evenly balanced due to me placing two hosts into maintenance mode to perform firmware updates, as you can see from the screenshot on the right, this has also triggered an alarm in vCenter.
A really cool feature of the Health Service is the “Ask VMware” button, simply highlight an issue and click the button and it will load up a VMware Knowledgebase article telling you what the issue means, why it has occurred and steps to remediate, as many of you know, I come from a support background and spent a good few years in VMware Support so the whole ability to self help and be provided with the right information straight away at the click of a button can 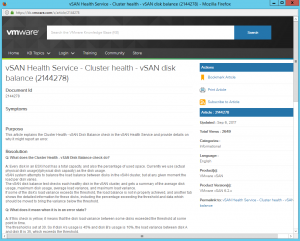 be a huge time saver in my opinion. There is a KB article for every section of the Health Service and as you can see from the screenshot on the left for my disk balance warning, there is quite a lot of detail in each KB article and the resolution steps are well documented and easy to follow. If after you have followed the steps in the KB and your issue still persists, remember to include in your support request that you have followed the KB Article so you are not asked to run through it again as part of troubleshooting.
be a huge time saver in my opinion. There is a KB article for every section of the Health Service and as you can see from the screenshot on the left for my disk balance warning, there is quite a lot of detail in each KB article and the resolution steps are well documented and easy to follow. If after you have followed the steps in the KB and your issue still persists, remember to include in your support request that you have followed the KB Article so you are not asked to run through it again as part of troubleshooting.
When you have deployments such as a 2-Node ROBO or a Stretched Cluster, you do not have to tell the Health Service about this, it will automatically detect and populate the appropriate health checks such as Site to Site latency and witness connectivity.
Critical Patch Updates – The Online Health Service also has the ability to make you aware of a critical patch release, as part of the “Build Recommendations” element of the Health Service, so as a critical patch is released, the online health service will dynamically slip entries into the UI to alert you of the release, in my opinion this is so much better than waiting for an email notification. The benefit for this is that it can be tailored for your environment, so you are not receiving notifications for updates that are not applicable to your environment.
A question I get quite often is how frequent does the Health Service report, the simple answer is by default it is designed to check the health every 60 minutes, in my environment I have this set to the lowest value which is 15 minutes, however, if there is a critical issue for example, a host failure, network connectivity issue or disk failure then the health service will update with this information pretty instantly, it will not wait for the next refresh cycle and again you will see vCenter alarms triggered for the events.
vRealize Operations
Now I have to admit, I am not a vROPS specialist in any way, shape or form, but I have deployed vROPS in my demo environment and have got the vSAN dashboards operational pretty easily without any challenges. Now to be clear I am using vROPS 6.6.1 which has the built in native vSAN dashboards which were not present in earlier versions and required you to use the vSAN Storage Management pack to enable the capturing of vSAN Metrics, below is a screenshot showing the default metrics reported in then vSAN Operations Overview dashboard
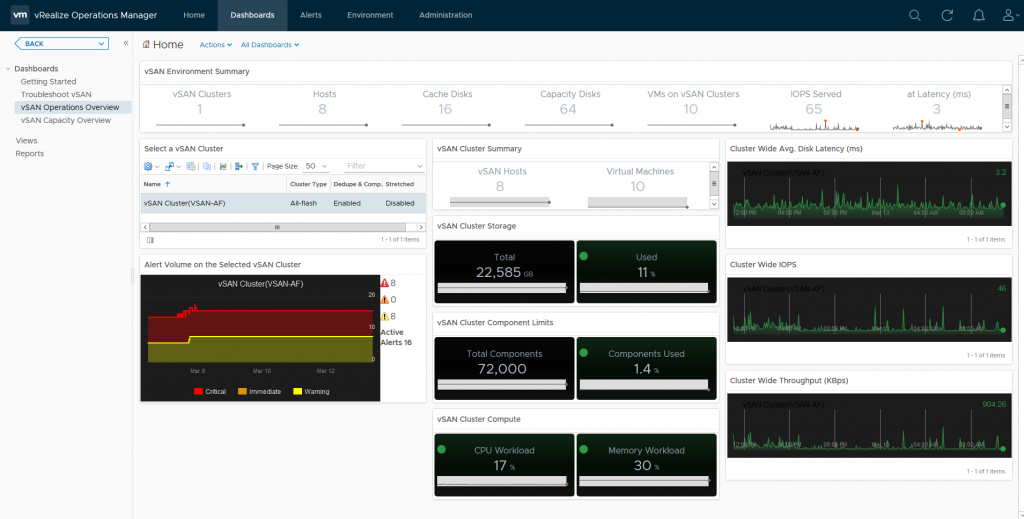
One immediate advantage that vROPS has over the vSphere UI is that vROPS can display a holistic view of all your vSAN clusters, whereas the vSphere UI is only showing you the status for the cluster that is in focus, so if I had multiple vSAN clusters deployed they would all be listed here in this single dashboard which makes operational life that little bit easier.
You can see there’s a wealth of information at your fingertips from an operational perspective, you can immediately see how your cluster(s) are performing as well as any potential issues that have triggered alarms, which then leads us to the Troubleshooting Dashboard, and here you can immediately see the reason for my 8 “Red” alerts:
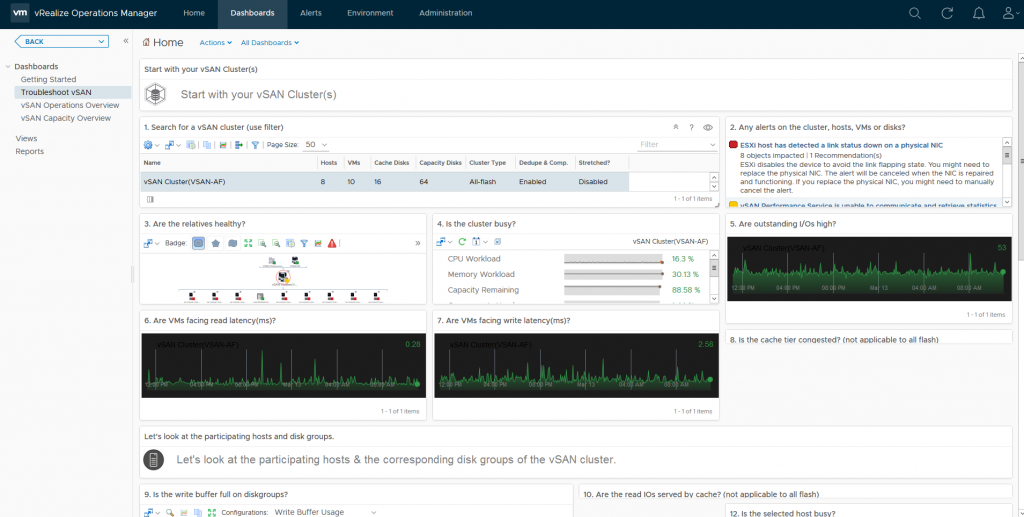
As you can see, just like the Operations Overview dashboard, the Troubleshooting dashboard has a lot of information, this dashboard is designed to allow you to drill down into specific areas and components within vSAN, provide you heatmaps on various areas such as disks for example which when a heatmap is red it will draw your attention, for example if I was to double click on one of the green squares in section 9 which is labelled “Is the write buffer full on diskgroups” it will take me to that specific cache disk:
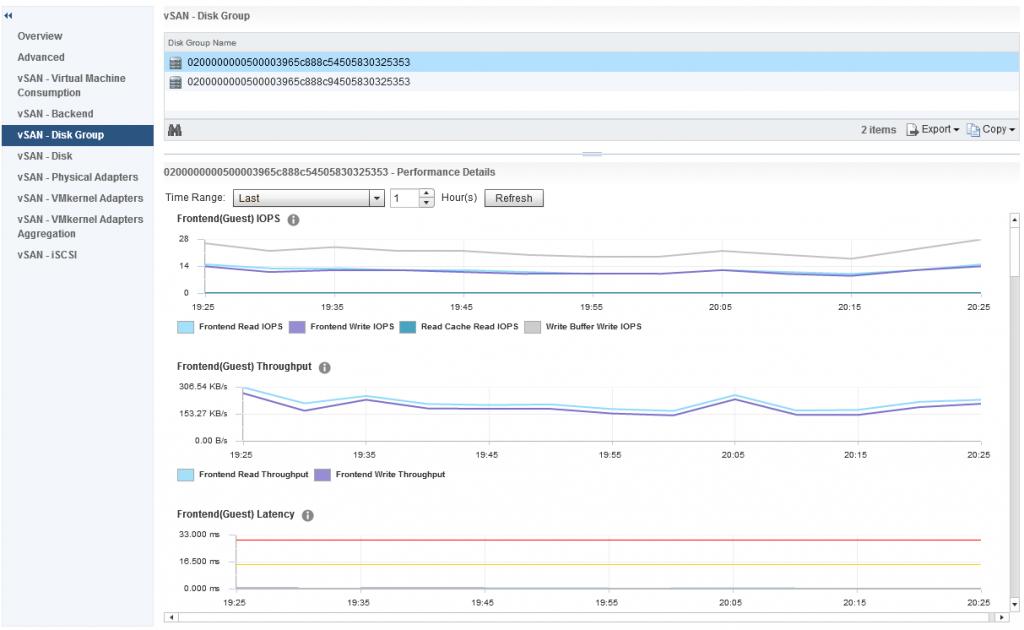
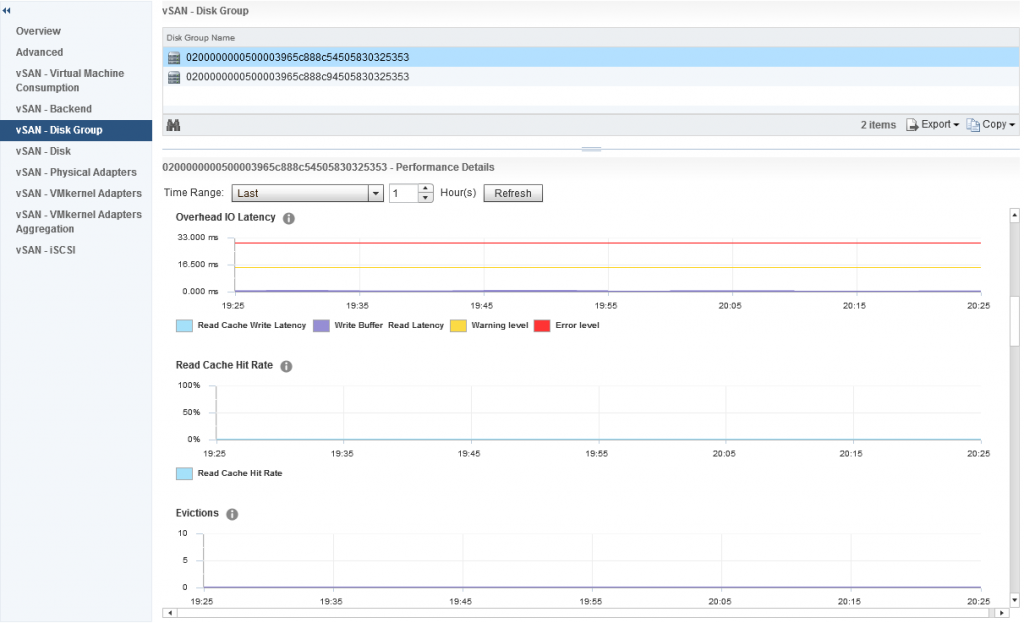
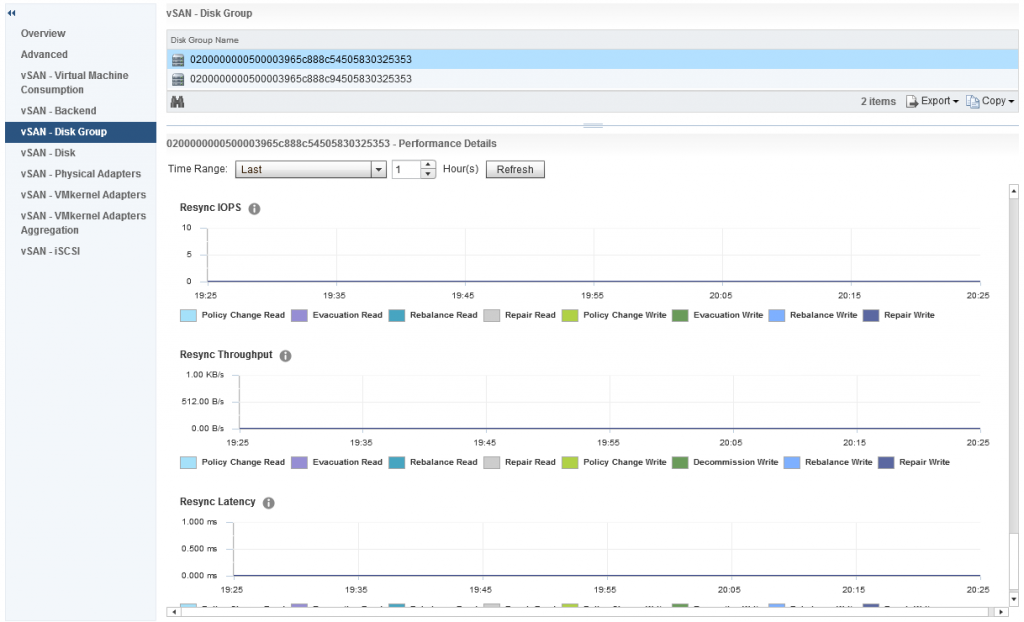
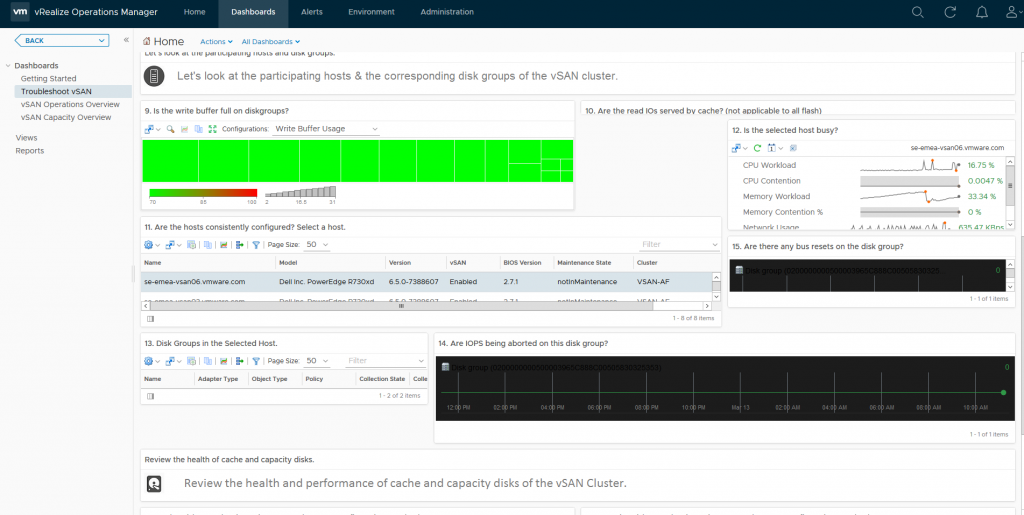 Which takes me to a dashboard specific to that disk group and provides me the following metrics:
Which takes me to a dashboard specific to that disk group and provides me the following metrics:
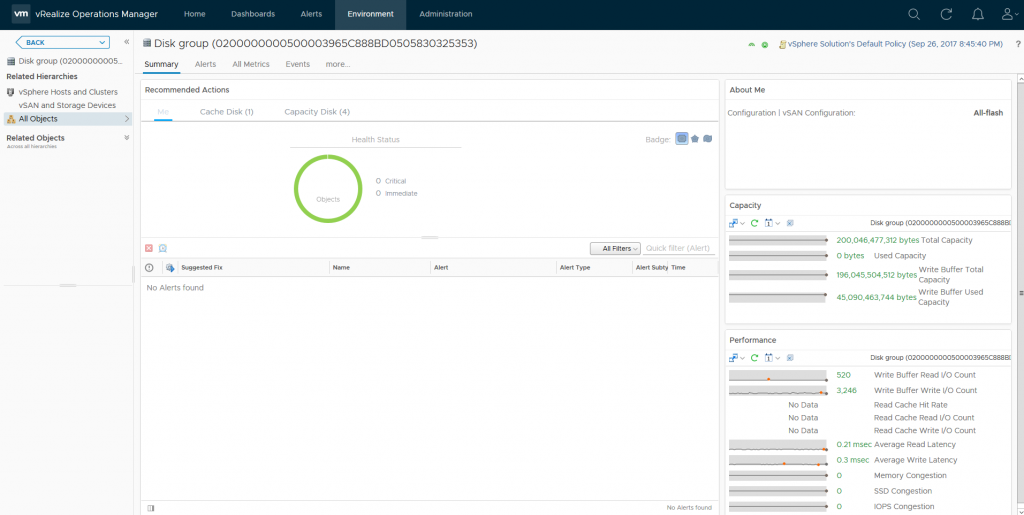 As you can see from the above screenshot I can see various important information about my disk group, and if the heatmap was red for this specific disk group I would be able to easily see why based on the metrics presented to me, in my case my disk group is healthy.
As you can see from the above screenshot I can see various important information about my disk group, and if the heatmap was red for this specific disk group I would be able to easily see why based on the metrics presented to me, in my case my disk group is healthy.
There is another dashboard in vROPS called Capacity Overview which I will cover on another Day-2 Operations post based around capacity reporting, so watch out for that one.
So as you can see there are immediately advantages and disadvantages of using the Health Service over vROPS and vice versa, in my opinion I think both tools are important in day to day operations and being able to use both tools provides you with the toolset to effectively manage your environments easier.
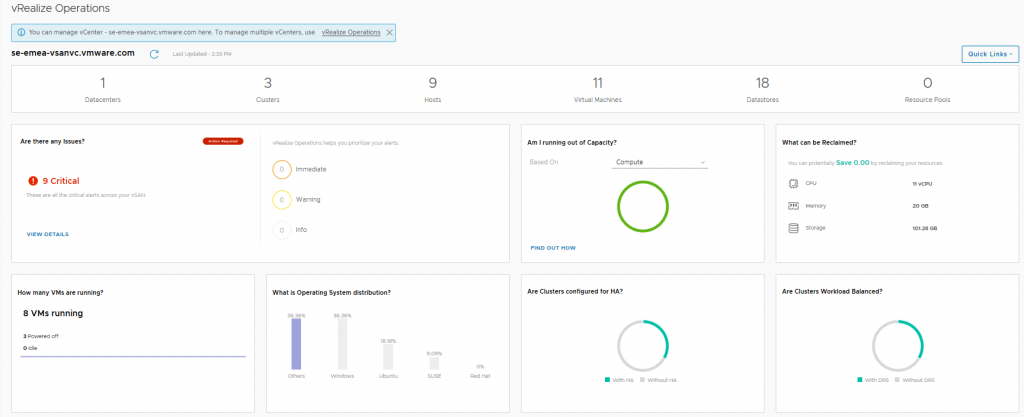
 Now the above three dashboards will no longer be available after the 90 day trial period has expired, and also the link to the vRealize Operations appliance will not be functional either, but after the 90 day trial period has expired, the following three vSAN Dashboards will still be fully functional and available, so let’s look at those in a bit more detail:
Now the above three dashboards will no longer be available after the 90 day trial period has expired, and also the link to the vRealize Operations appliance will not be functional either, but after the 90 day trial period has expired, the following three vSAN Dashboards will still be fully functional and available, so let’s look at those in a bit more detail: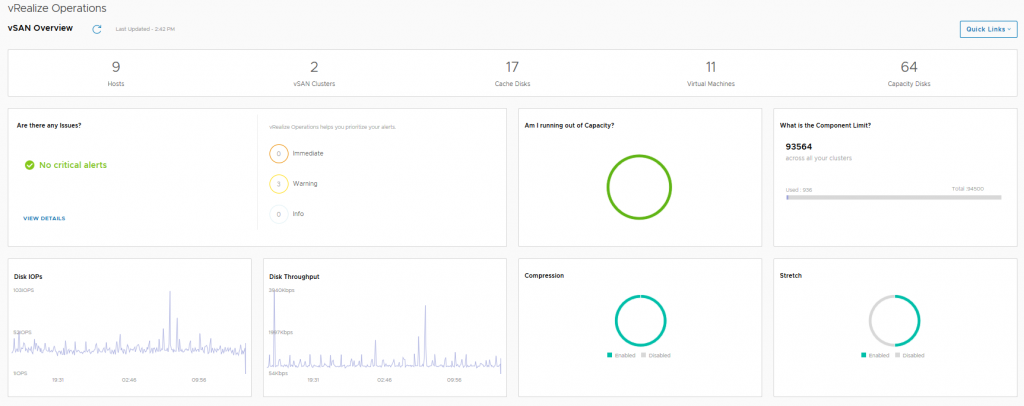 The vSAN Overview dashboard, like the vSphere overview dashboard, displays information at a holistic level for all of your vSAN Clusters within this particular vCenter server, you will see that the dashboard provides information on how many clusters are running dedupe/compression, or how many of the clusters are a Stretched Cluster for example. The dashboard also shows if you need to investigate any current alerts (yes I cleaned up the failed disk before grabbing this screenshot).
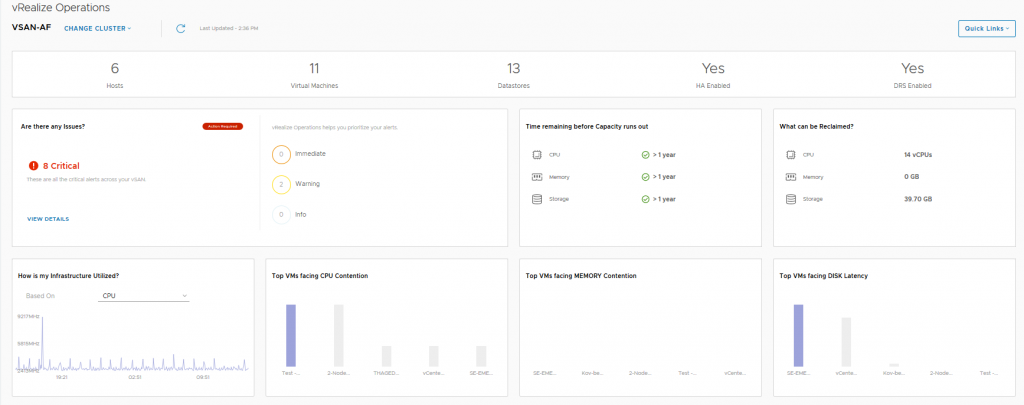
The vSAN Overview dashboard, like the vSphere overview dashboard, displays information at a holistic level for all of your vSAN Clusters within this particular vCenter server, you will see that the dashboard provides information on how many clusters are running dedupe/compression, or how many of the clusters are a Stretched Cluster for example. The dashboard also shows if you need to investigate any current alerts (yes I cleaned up the failed disk before grabbing this screenshot).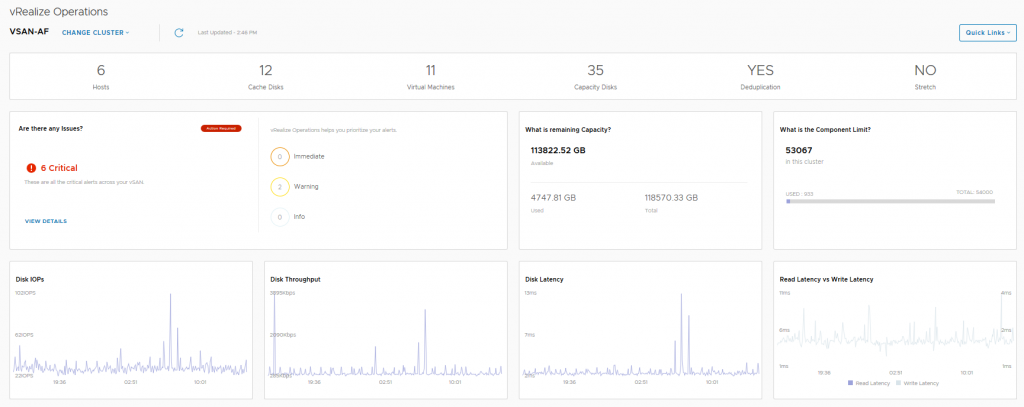 In this dashboard we see information pertaining to a specific cluster, we can see that I have 6 critical alerts which we will take a look at next, but there are some key metrics here that from an operational perspective are pretty important from a day-2 operations standpoint:
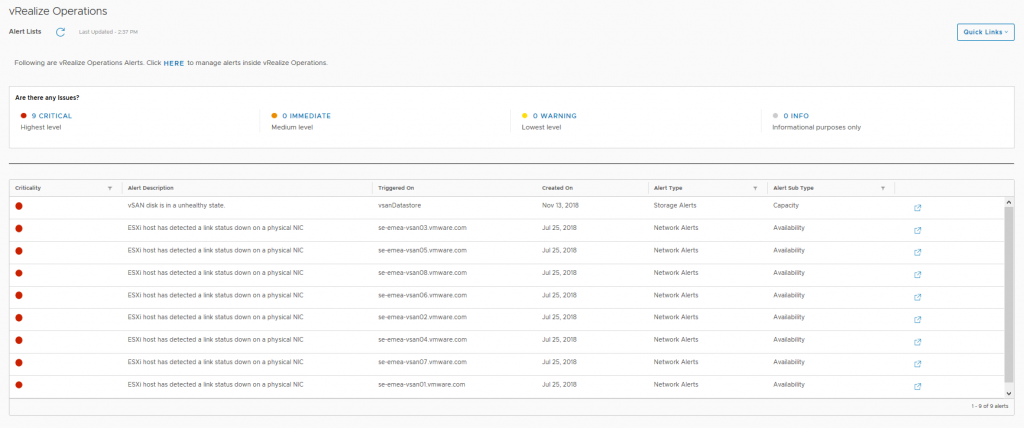
In this dashboard we see information pertaining to a specific cluster, we can see that I have 6 critical alerts which we will take a look at next, but there are some key metrics here that from an operational perspective are pretty important from a day-2 operations standpoint: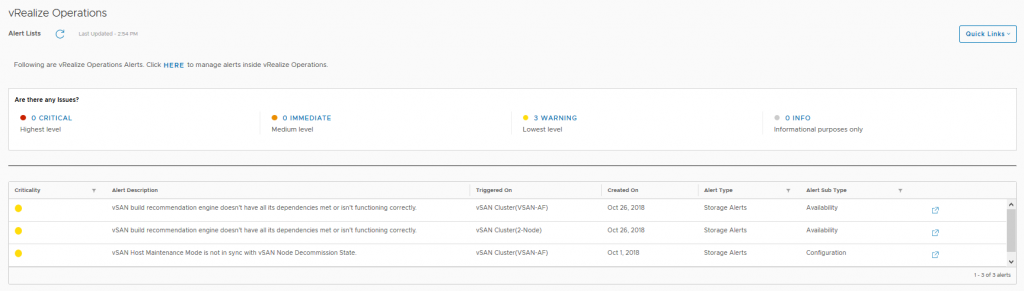 Here we can see the current alerts that have been triggered for each cluster which may need to be addressed, the critical alerts previously highlighted in the cluster view were all related to a network redundancy lost when I was troubleshooting packet loss on the physical switch.
Here we can see the current alerts that have been triggered for each cluster which may need to be addressed, the critical alerts previously highlighted in the cluster view were all related to a network redundancy lost when I was troubleshooting packet loss on the physical switch.